ECON 140W - Week 1
Class 1 - Jan. 6, 2026
What is Economics?
- Inflation
- We want this to go back to being boring
- GDP
- Measure of output in the economy, why it's good, why it's not great for everything
- Unemployment
- Technically, can't be unemployed as a student
- Monetary policy
- We should have enough knowledge by the end of the course to write our own monetary report like the Government of Canada does
- Fiscal policy
- Taxes
- Spending
- What is the problem with government debt? Issues/benefits or running a deficit
- Investment
- Building up a physical investment like a factory
- Financial investments like bonds, stocks, international foreign currency exchange
Long-Run Trends and Fluctuations
Total GDP, Canada
Recession dates: 1982, 1991, 2008, 2020
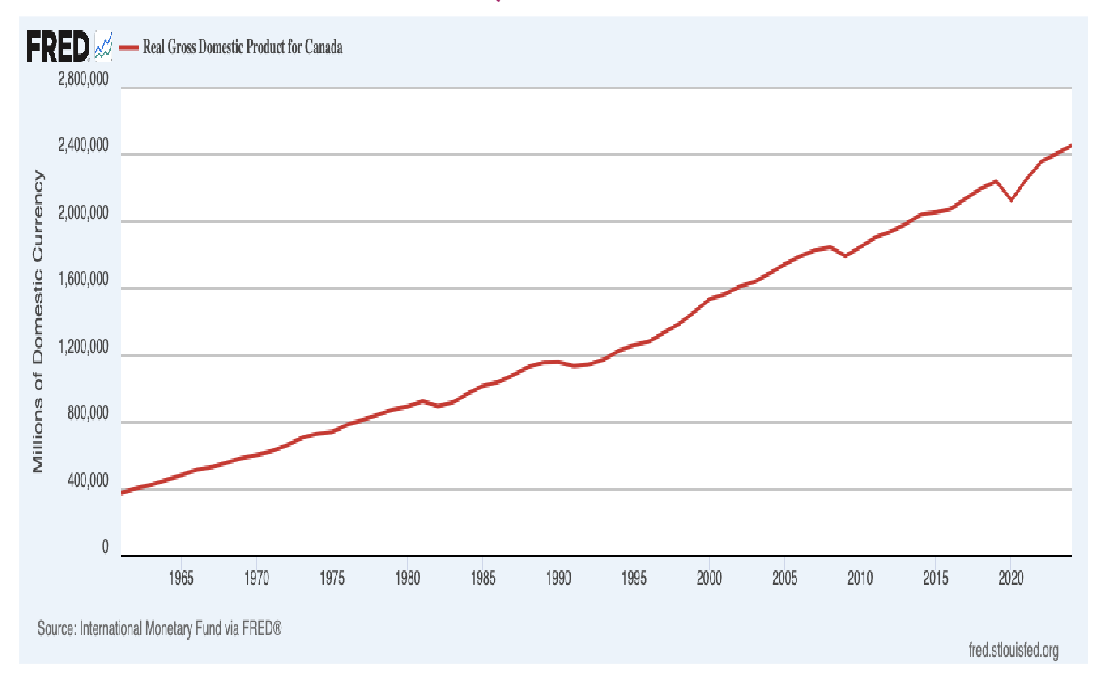
Reasons for growth:
- Partly because we're better at producing stuff
Growth rate, GDP, Canada
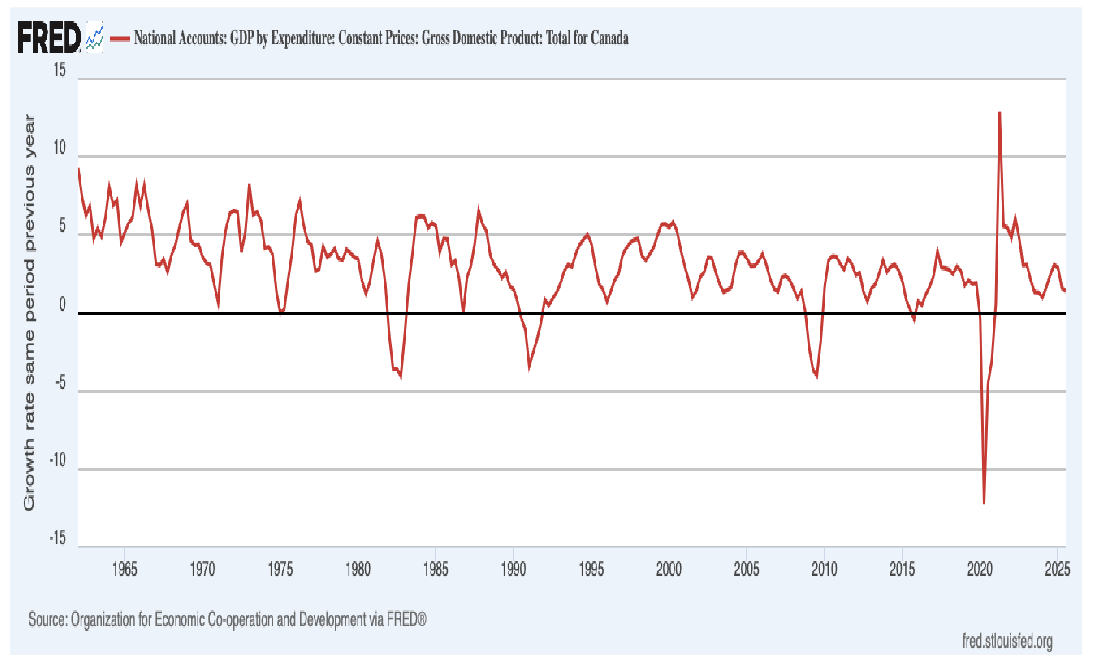
Reasons for growth:
- When growth rate negative, recession! woohooo
Policy Issues
- Fiscal policy
- Tax rates, government spending, trade policy
- Monetary policy
- Interest rates, currency regimes, international finance
- Most policy choices involve tradeoffs
- Lenders vs. borrowers
- If interest rates go up, as a lender you make more but borrowers you lose more
- Homeowners vs. renters
- When housing prices go up, theof Canadians that own houses are happy
- This is a reason students have a hard time in EC 140, because there's not much intuition that can be used - Short-term - Unemployment vs. inflation (maybe?)
- If Bank of Canada lowers interest rates which causes more unemployment
- Long-term - Growth vs. Inequality (maybe?)
- Lenders vs. borrowers
Choices Among Alternatives
GNI per capita, 2010 USD
Gini index (inequality)
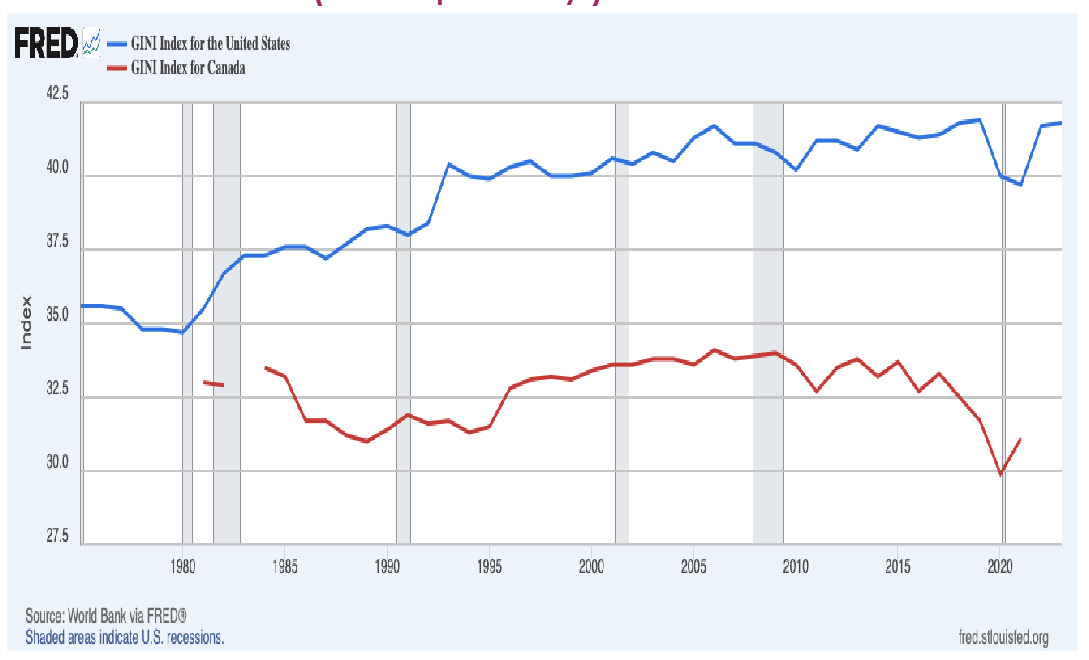
This ^ is bad, because people in Canada will want to go to USA because they can make more.
Time Horizon and Economic Policy
- What are the key policy issues over:
- The next 4 months - by the end of the term
- Not much will change
- Monetary policy and economic management
- The next 4 years - during your degree
- Fiscal policy, government debt and deficits, housing prices
- Government invests a lot in education
- The next 40 years or longer
- Economics growth, productivity, and the future of work
- The next 4 months - by the end of the term
Critical Questions - Housing Market
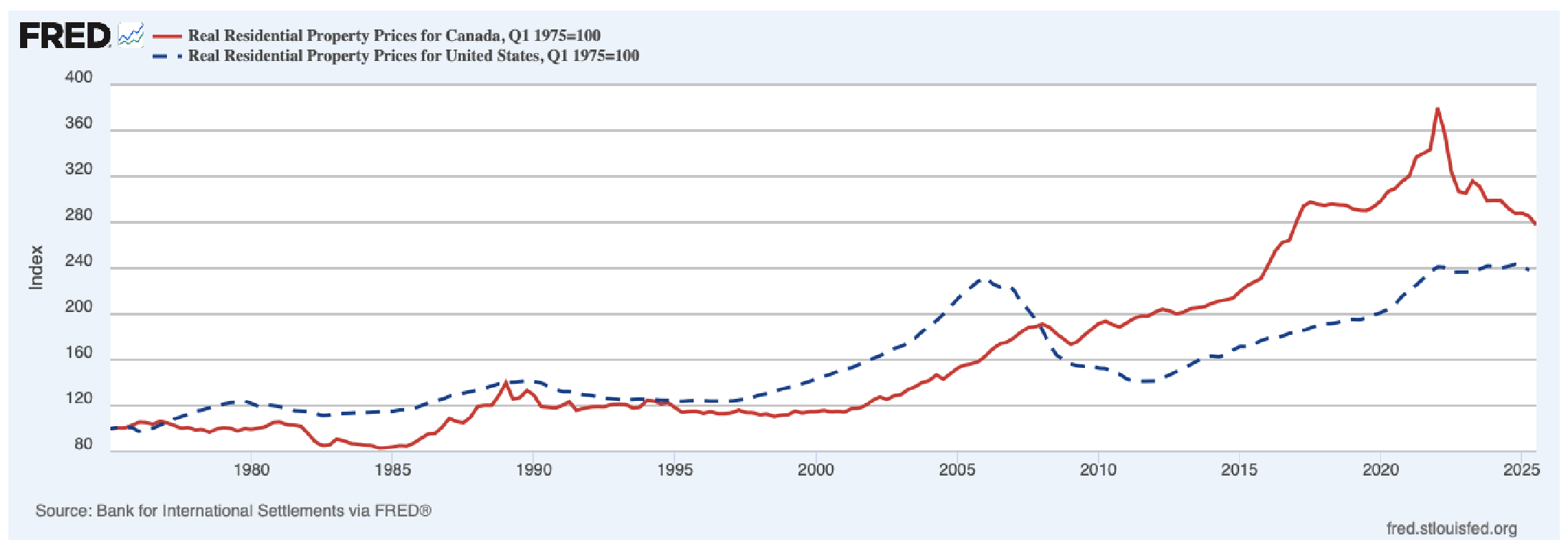
2008 Financial crisis: Went down by half - led to global recession
- In the past 3 years, housing prices have decreased in Canada but not a global recession because Canada is small
Critical Questions - Youth Unemployment
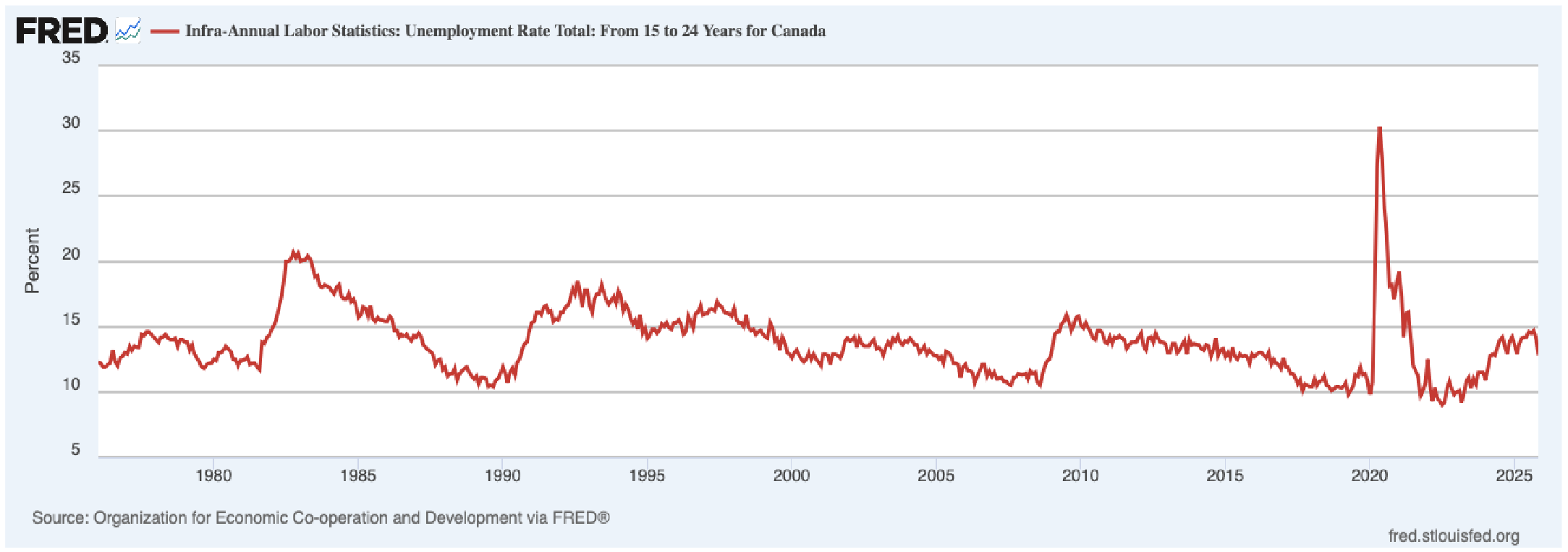
Has fluctuated around but in October/November has dropped. We're at 15% right now. We have long term decline in unemployment rates with short term inclines.
Sources
- Macroeconomics is about the link between theory and data
- Key data sources in this course:
- Statistics Canada (https://statcan.gc.ca)
- Daily releases of new information
- U.S. Federal Reserve (https://fred.stlouisfed.org)
- World Bank (https://data.worldbank.org)
- Statistics Canada (https://statcan.gc.ca)
- We aren't expected to memorize data, but one of Ken's goals is that we occasionally check to see if our assumptions are correct
Class 2 - Jan. 8, 2026
Population in Canada
Ken thinks Macroeconomics starts in Canada
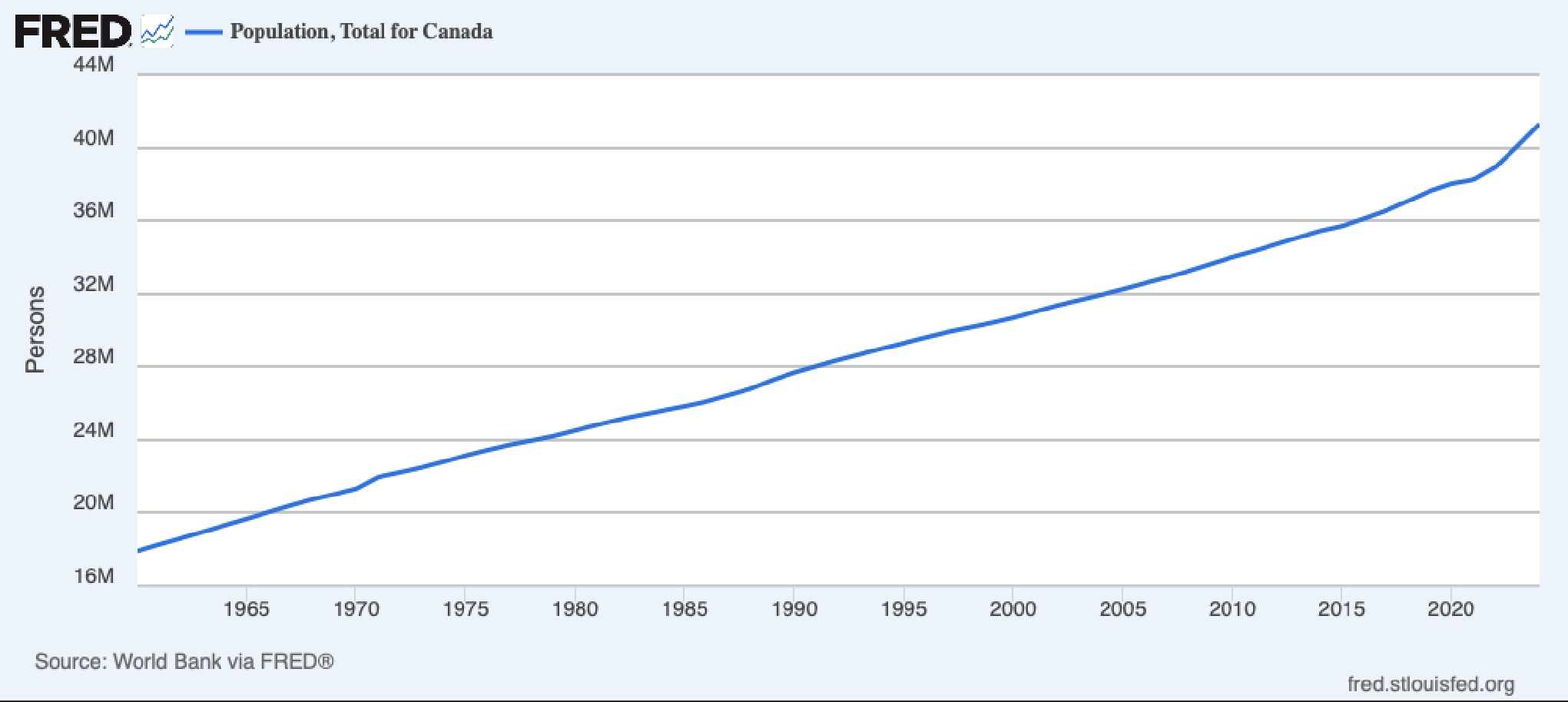
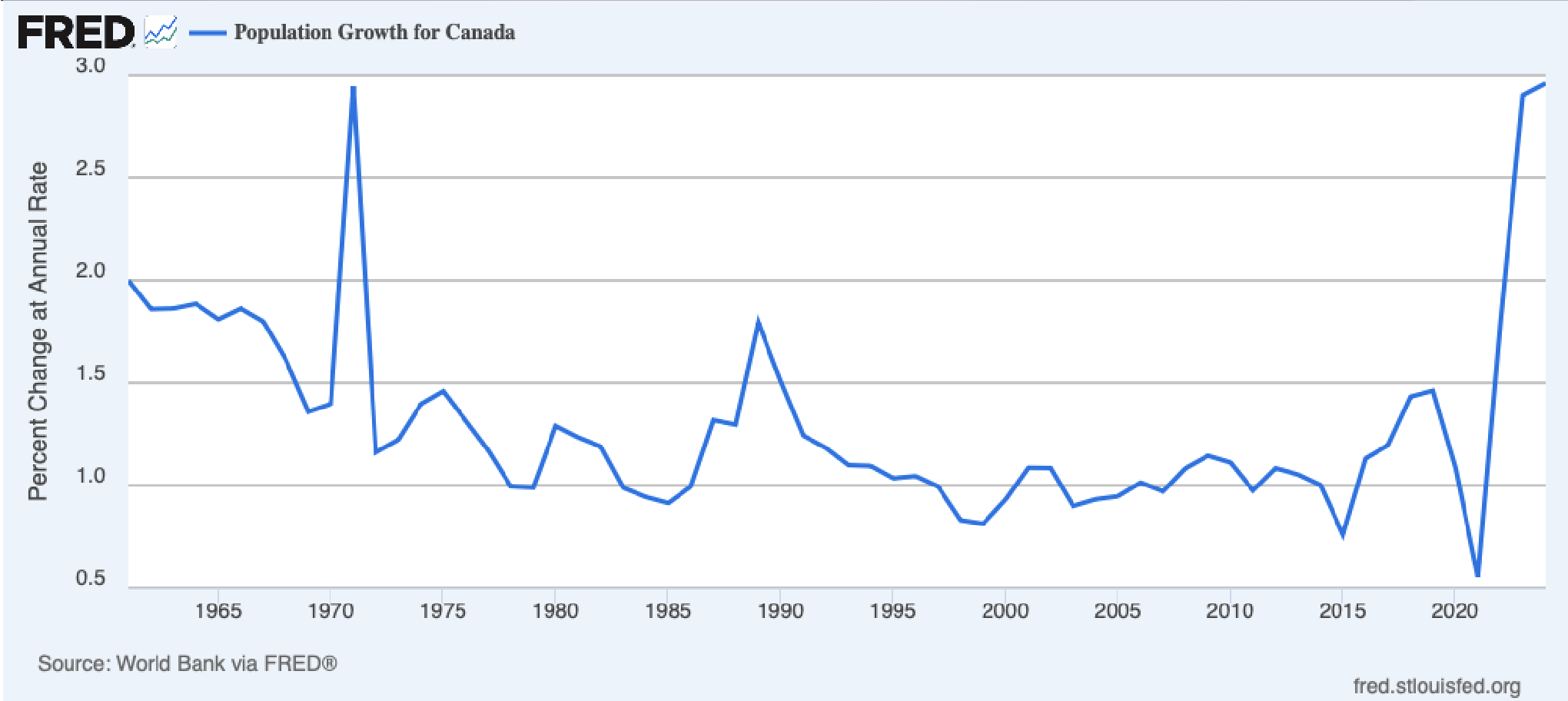
Population Growth in Canada
Canada does a bad job at tracking population. Canada doesn't know when you left the country.
The spike in 1971 is because they realized that they miscounted really badly.
Canada Inflation Rate - 1915-2023
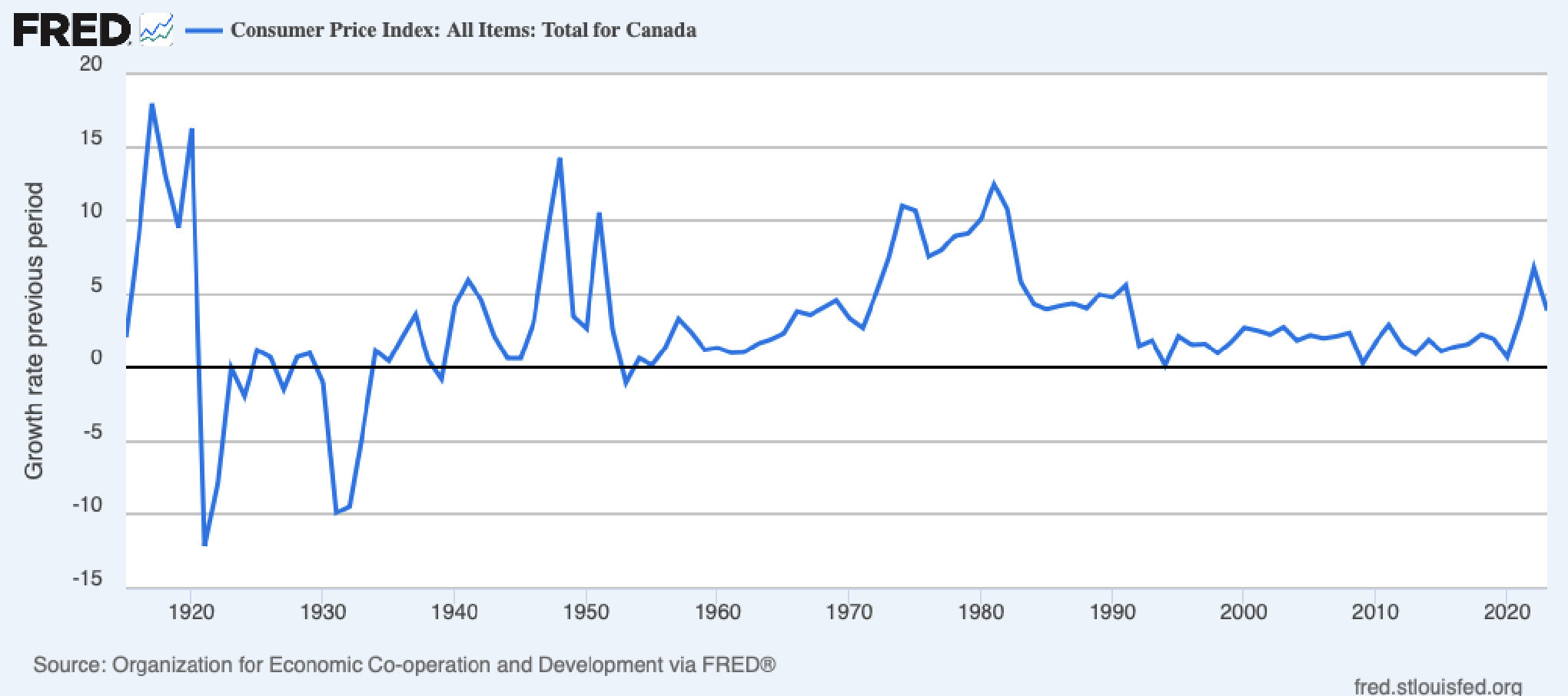
- During the first world war, Canada started measuring things quite a bit. This is because during wartime, economics goes wild.
- Negative inflation is almost never good. (Post WWI and The Great Depression above).
- Ken won't spend much time talking about pre-1950 when it comes to data because it wasn't amazing and there was 2 world wars, etc.
- There's a big boost in oil control during the 1970s leading to US going off the gold standard and thus high inflation.
Canadian - Unemployment
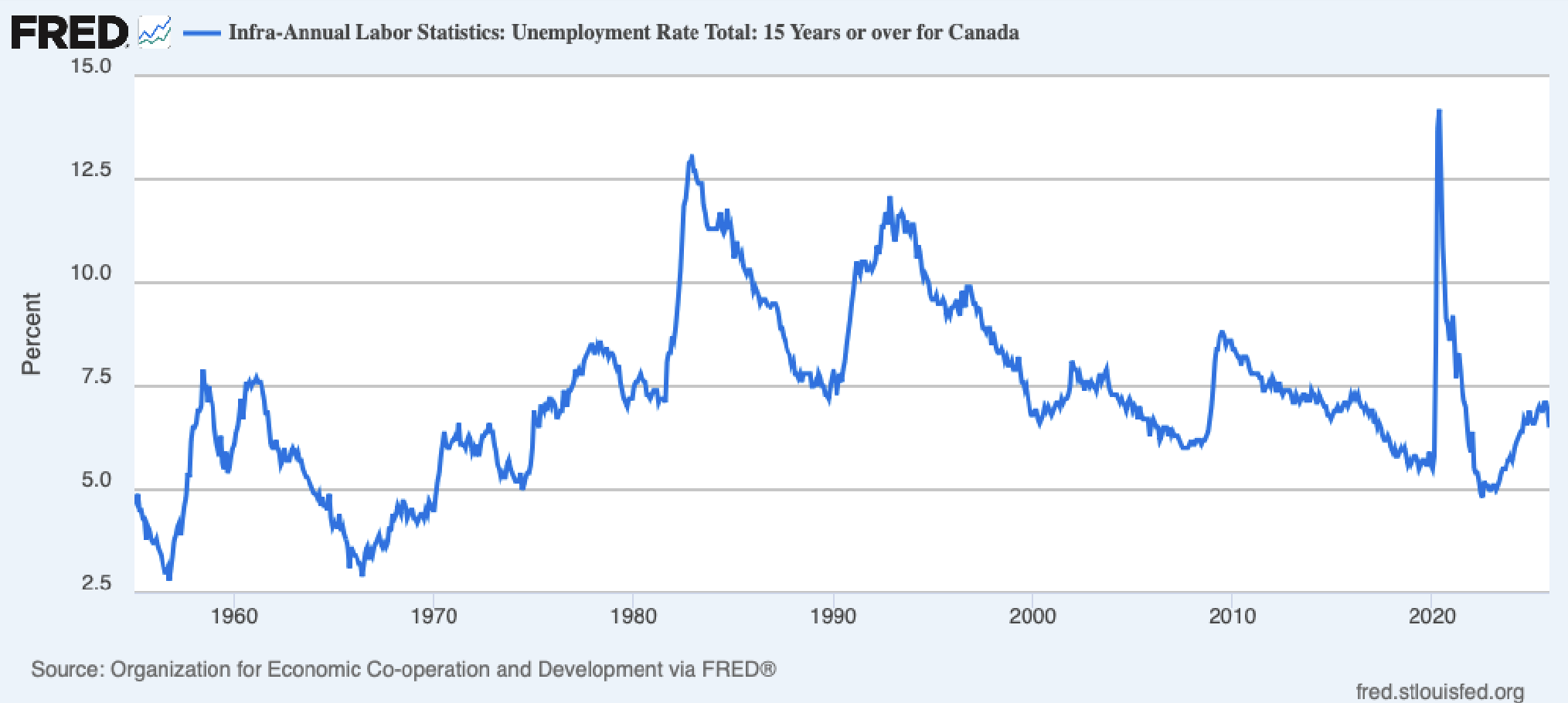
- Statistics runs a labour survey - they survey 60,000 people and ask them if they are employed and a bunch of questions.
- Unemployment is the fraction of people who want a job and can't have one.
- Global financial crisis didn't directly hit Canada
- Hit finance industry but they don't really lose their jobs
Core Age Employment and Participation
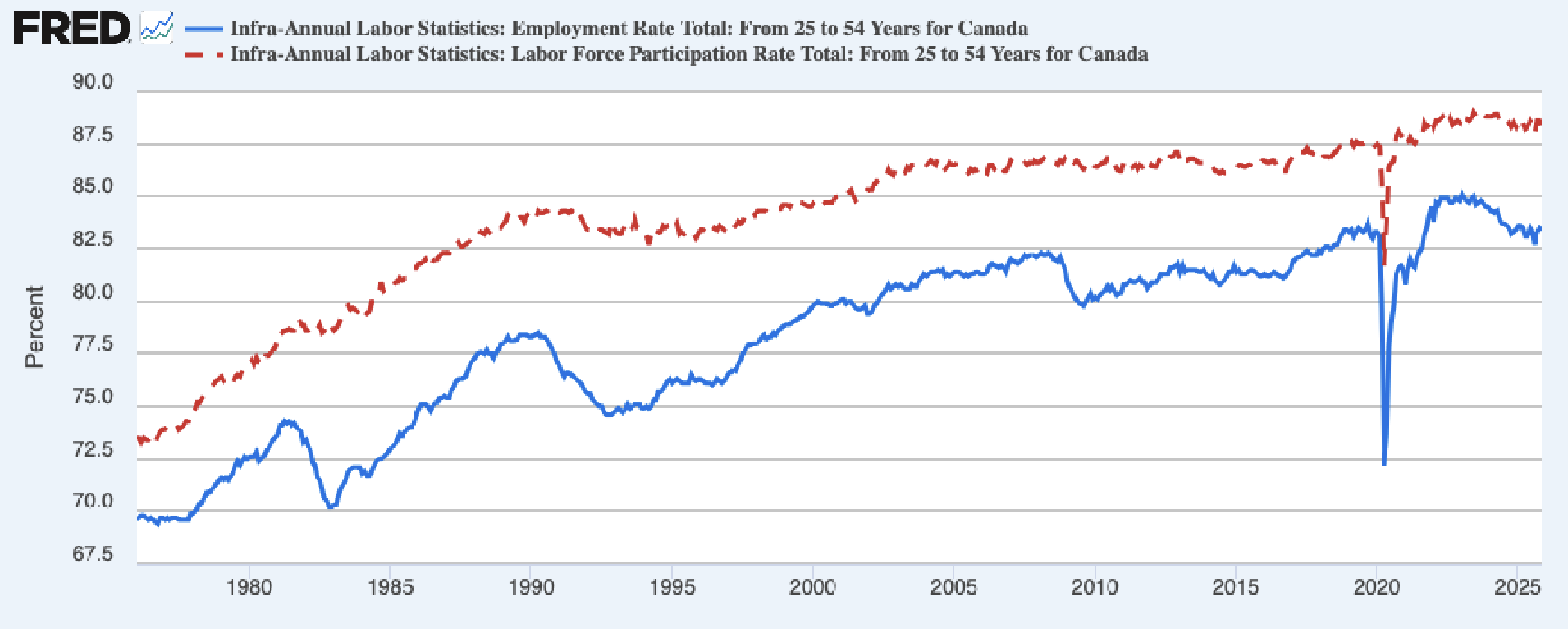
- The difference between red and blue are loosely unemployment rate.
- Rise up until 1990 is woman entering the workforce
Canadian Interest rates
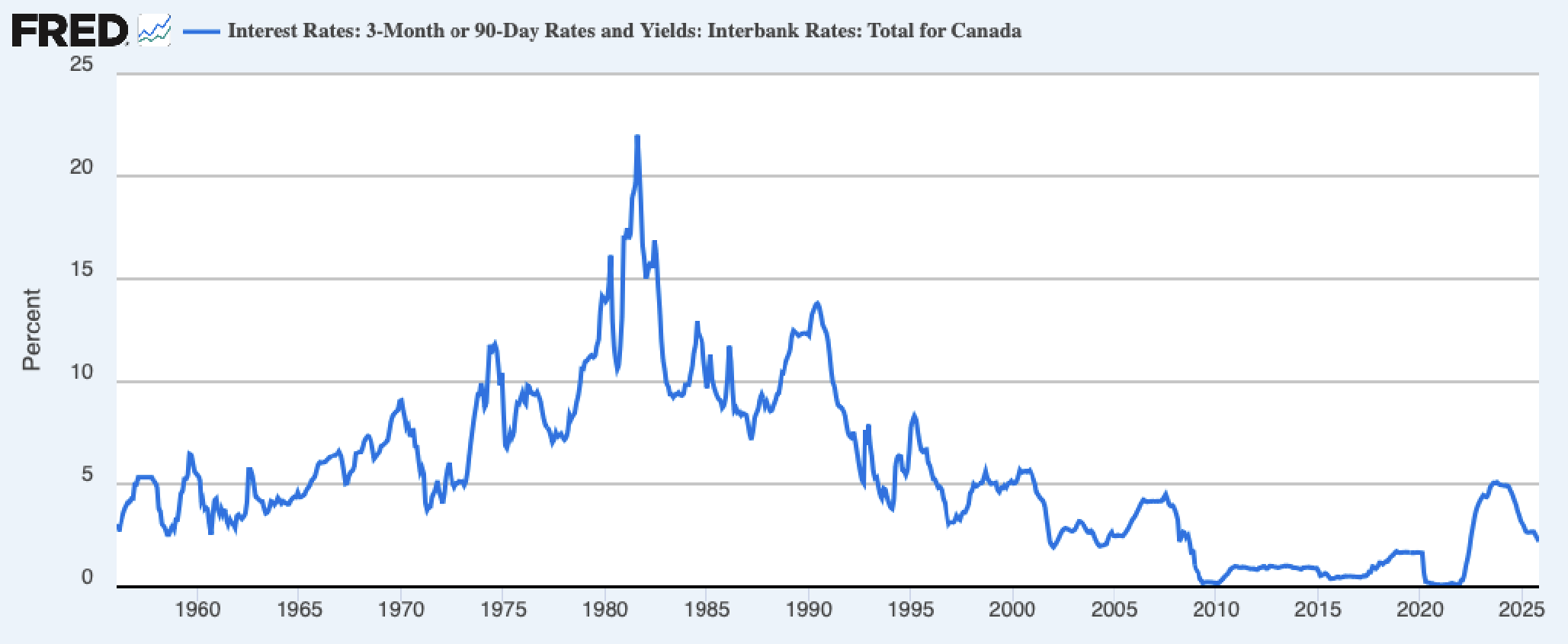
When there is really low interest rates, people borrow money:
Household Debt
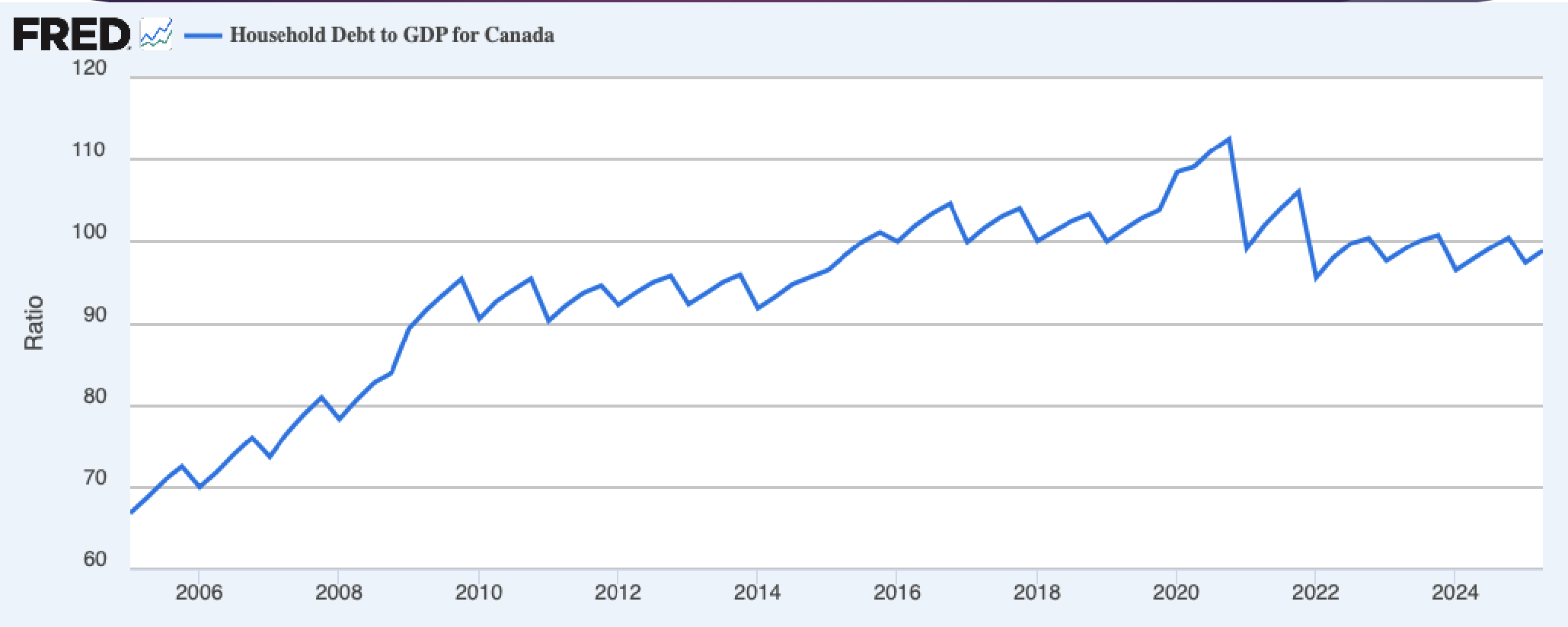
Canada in Comparison with the U.S.
- U.S. is decent comparison but not the only one
- Canada is strongly affected by the United States
- It also never serves as a natural comparison
- We should also look at other countries
- Common error to act like U.S. is the only Alternatives
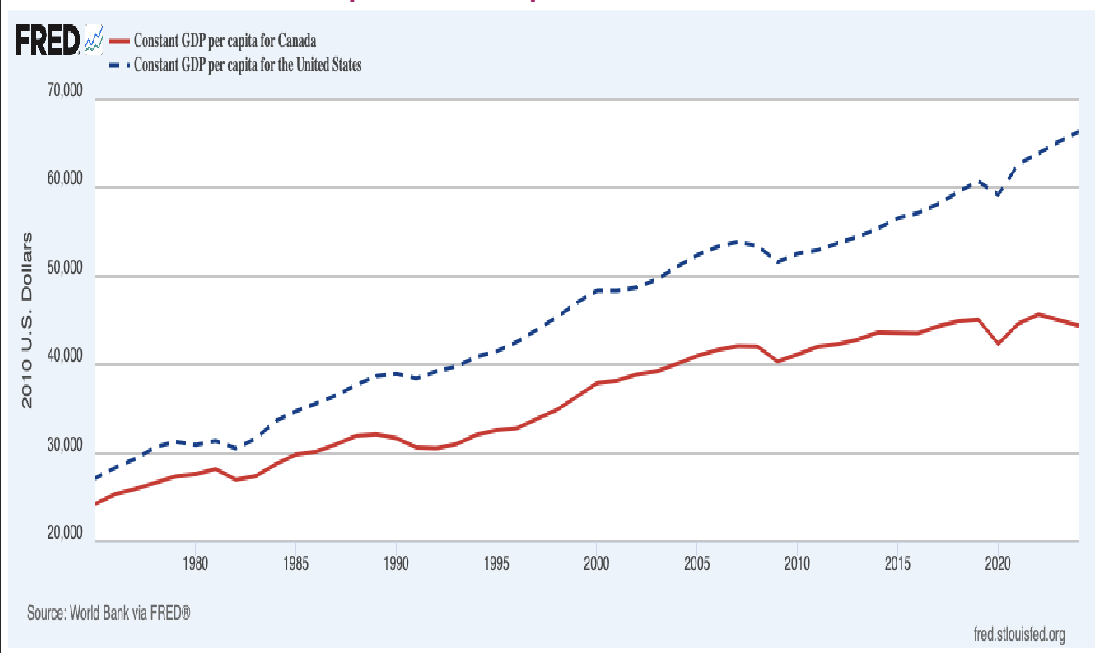
GDP per capita - Canada vs. the U.S.
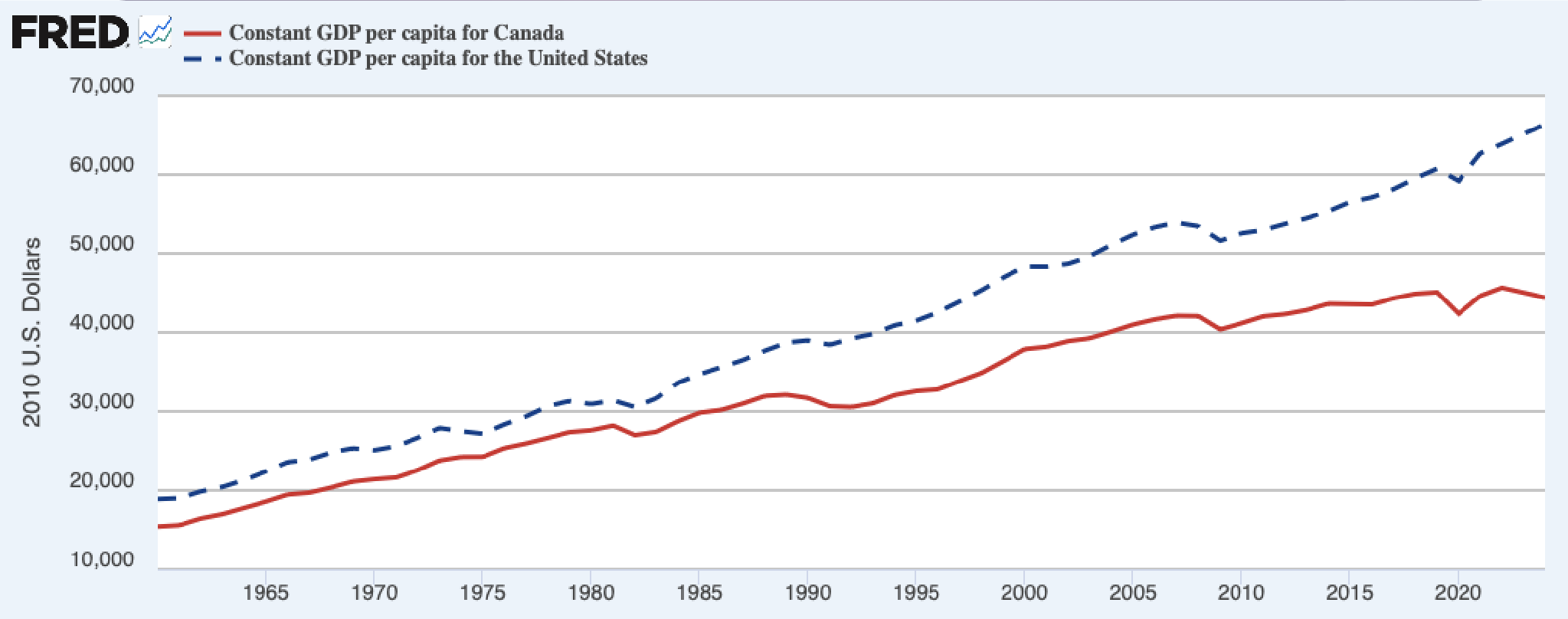
Canada vs. the U.S. - Labour Force
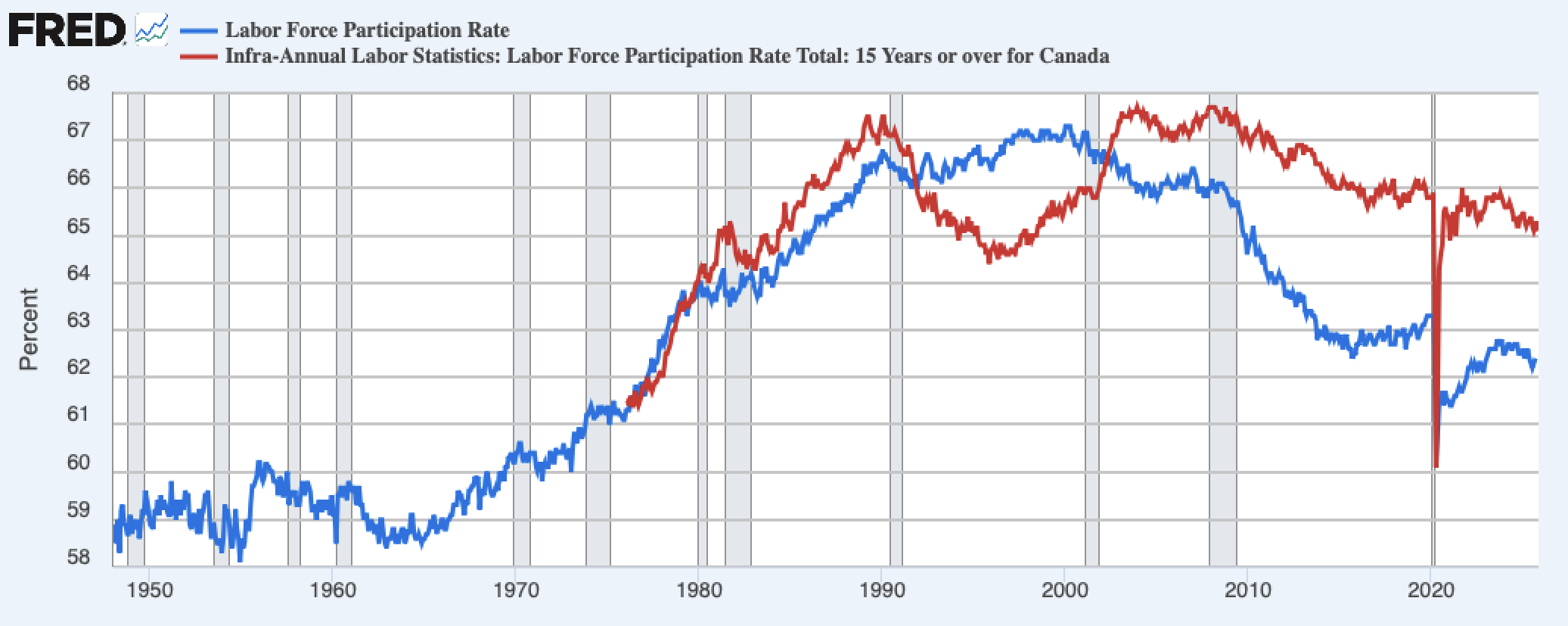
- In 1990s, the dip is due to many factors
- The steady decline since 2010s is baby boomers retiring
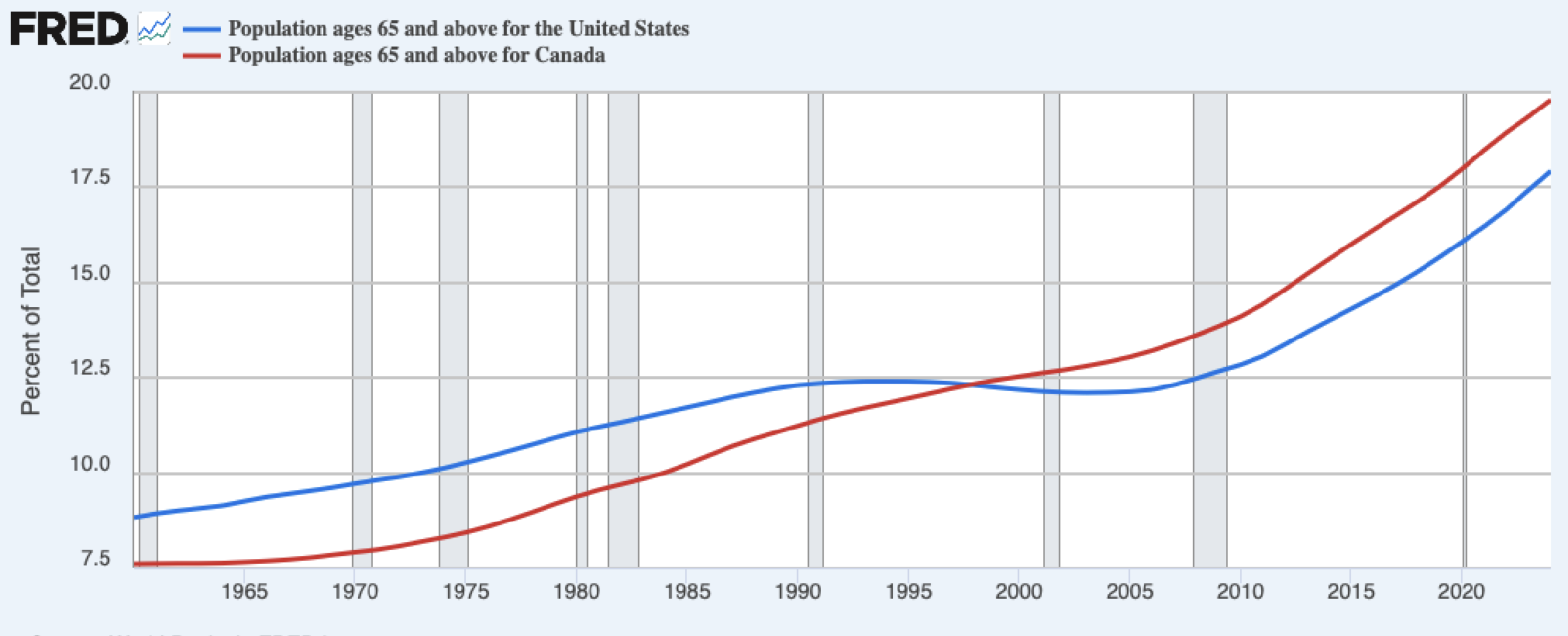
The Aging Population